Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hattori, Takanori
Yukuatsu Gijutsu, 61(7), p.29 - 35, 2022/07
As an example of the application of hydraulic technology, the 6-axis type multi-anvil press "ATSUHIME" in the J-PARC ultra-high pressure neutron diffractometer PLANET and the research on hydrogen in the Earth's core using them are introduced.
Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Machida, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Okazaki, Nobuo*
Nihon Kessho Gakkai-Shi, 59(6), p.301 - 308, 2017/12
PLANET is a neutron beamline dedicated to high-pressure experiments. Combining the intense neutron source of J-PARC and high-pressure devices designed for time-of-flight powder neutron diffraction enables precise structure analysis of crystal, liquid and amorphous solids over wide pressure and temperature region of 0-20 GPa and 77-2000K. This beamline is effective for various studies in geophysics, planetary science, physics and chemistry. This paper overviews the beamline and introduces recent results obtained at PLANET.
Niimura, Nobuo; Chatake, Toshiyuki; Ostermann, A.; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tanaka, Ichiro
Zeitschrift f r Kristallographie, 218(2), p.96 - 107, 2003/03
r Kristallographie, 218(2), p.96 - 107, 2003/03
no abstracts in English
Fernandez-Baca, J. A.*; Dai, P.*; Wakabayashi, Nobuyoshi*; Plummer, E. W.*; Katano, Susumu; Tomioka, Yasuhide*; Tokura, Yoshinori*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, Vol.70, Supplement A, p.85 - 87, 2001/00
no abstracts in English
Kurihara, Kazuo; Tomoyori, Katsuaki; Tamada, Taro; Kuroki, Ryota
no journal, ,
Many of membrane proteins and protein complexes have larger molecular weight and then unit cells of their crystals have larger volume. Therefore, our group had designed the diffractometer which is able to cover such a crystal with large unit cell volume (target lattice length: 250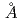 ). This proposal was accepted by Neutron Instrument Program Review Committee of J-PARC in September 2012. Larger unit cell volume causes a problem to separate spots closer to each other in spatial and time distribution in diffraction images. Therefore, our proposed diffractometer adoptted longer camera distance (800mm) and decoupled moderator as neutron source which has shorter pulse width. The neutron guide tube was designed to use limited surface of the decoupled moderator with high luminescence (40mm high
). This proposal was accepted by Neutron Instrument Program Review Committee of J-PARC in September 2012. Larger unit cell volume causes a problem to separate spots closer to each other in spatial and time distribution in diffraction images. Therefore, our proposed diffractometer adoptted longer camera distance (800mm) and decoupled moderator as neutron source which has shorter pulse width. The neutron guide tube was designed to use limited surface of the decoupled moderator with high luminescence (40mm high  60mm wide) whose luminosity is 1.24 times as high as that of average of the whole surface in the range over 2.86
60mm wide) whose luminosity is 1.24 times as high as that of average of the whole surface in the range over 2.86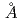 of wavelength. In addition, ellipsoidal shape in vertical design of the guide was adopted to suppress the number of neutron reflections at the guide mirror accompanying reduction of neutron intensity. In the horizontal design, curved shape was in part introduced to eliminate unnecessary
of wavelength. In addition, ellipsoidal shape in vertical design of the guide was adopted to suppress the number of neutron reflections at the guide mirror accompanying reduction of neutron intensity. In the horizontal design, curved shape was in part introduced to eliminate unnecessary  -rays and short-wavelength neutrons. According to ray-tracing simulation by McStas code, neutron flux at the sample position is estimated to be 5
-rays and short-wavelength neutrons. According to ray-tracing simulation by McStas code, neutron flux at the sample position is estimated to be 5 10
10 /cm
/cm /s in the wavelength range of 1.5
/s in the wavelength range of 1.5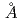 - 5.6
- 5.6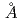 (first frame).
(first frame).
Kurihara, Kazuo; Tomoyori, Katsuaki; Tamada, Taro
no journal, ,
Many of membrane proteins and protein complexes have larger molecular weight and then unit cells of their crystals have larger volume. Therefore, our group had designed the diffractometer which is able to cover such a crystal with large unit cell volume (target lattice length: 250  ). This proposal was accepted by Neutron Instrument Program Review Committee of J-PARC in September 2012. Larger unit cell volume causes a problem to separate spots closer to each other in spatial and time distribution in diffraction images. Therefore, our proposed diffractometer adopted longer camera distance (800 mm) and decoupled moderator as neutron source which has shorter pulse width. The neutron guide tube was designed to use limited surface of the decoupled moderator with high luminescence (40 mm high
). This proposal was accepted by Neutron Instrument Program Review Committee of J-PARC in September 2012. Larger unit cell volume causes a problem to separate spots closer to each other in spatial and time distribution in diffraction images. Therefore, our proposed diffractometer adopted longer camera distance (800 mm) and decoupled moderator as neutron source which has shorter pulse width. The neutron guide tube was designed to use limited surface of the decoupled moderator with high luminescence (40 mm high  60 mm wide) whose luminosity is about 1.3 times as high as that of average of the whole surface in the wavelength range from 2.9
60 mm wide) whose luminosity is about 1.3 times as high as that of average of the whole surface in the wavelength range from 2.9  to 9.1
to 9.1  . Ellipsoidal and curved shape were introduced in the vertical and the horizontal design of the guide design, respectively, which provide maximum beam divergence of 0.8
. Ellipsoidal and curved shape were introduced in the vertical and the horizontal design of the guide design, respectively, which provide maximum beam divergence of 0.8 in vertical and 0.6
in vertical and 0.6 in horizontal, respectively, at the sample position. According to ray-tracing simulation by McStas code, neutron flux at the sample position is estimated to be 5
in horizontal, respectively, at the sample position. According to ray-tracing simulation by McStas code, neutron flux at the sample position is estimated to be 5 10
10 /cm
/cm /s in the wavelength range of 1.5
/s in the wavelength range of 1.5  - 5.6
- 5.6  (first frame).
(first frame).
Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Ohara, Takashi; Nakao, Akiko*; Hanashima, Takayasu*; Munakata, Koji*; Moyoshi, Taketo*; Kuroda, Tetsuya*; Tamura, Itaru; Oikawa, Kenichi; Kaneko, Koji; et al.
no journal, ,
SENJU is a TOF-Laue type neutron single crystal diffractometer built at BL18 in J-PARC/MLF and has been in operation since 2012. This instrument is designed to perform precise structure analyses of inorganic materials, small molecular materials and magnetic materials under special environment. With this instrument, highly efficient measurements of a small single crystal can be achieved utilizing the high flux white neutrons provided by J-PARC and multiple 2-dimentional detectors. 4K-cryostat is one of the most commonly used sample environment devices which is equipped with a 2-axis rotators at the cold head. Owing to this functionality, one can measure several different orientations of a sample without moving the cryostat nor without taking the sample out. The superconducting magnet which can generate 7T at most offers very clean data since no Bragg reflections originated from the magnet appear in the low-momentum transfer region. The measured data will be analyzed with a software called STARGazer, which can cover the visualization of the data, data reduction to histogram files, determination of the orientation matrixes and integration of peak intensity for further structure analyses.
Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Machida, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*
no journal, ,
PLANET is a high-pressure neutron beamline recently constructed at J-PARC. The most characteristic features of the beamline are its high performance in obtaining clean data with almost no contamination of the signal from a sample container and wide accessible d-spacing range. The beamline is equipped with various high pressure presses, such as the large six-axis multi-anvil high-pressure press (ATSUHIME), Paris-Edinburgh presses, the low-temperature press and a diamond anvil cell. By using these devices, in-situ neutron diffraction experiments are possible over wide PT condition currently of 40-2000 K and/or up to 20 GPa. Combining these presses with the aforementioned beamline characters enables the precise structure determination not only of crystalline materials but also of liquid and amorphous materials. In this presentation, I will introduce the specification of the beamline and recent results obtained at PLANET.
Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Arima, Hiroshi*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Abe, Jun*; Machida, Shinichi*; Ouchi, Keiichi*; Okazaki, Nobuo*
no journal, ,
PLANET is a high-pressure neutron beamline recently constructed at MLF in J-PARC. Most characteristic feature of the beamline is to possess the large six-axis multi-anvil high-pressure ATSUHIME press, which enables in-situ neutron diffraction under high pressure and high temperature condition up to 10 GPa and 2000 K. Smaller presses, a Paris-Edinburgh press and Mito cell, are also available and the accessible PT conditions with each device are 20 GPa at room temperature and 5 GPa at 77 K, respectively. The beamline is equipped with incident slits and receiving collimators that eliminates parasitic scattering from the high-pressure cell assembly to obtain clean data. The high performance of the diffractometer and low-parasitic scattering characteristics enables precise structure determination of crystals and liquids under high pressure and temperature conditions. In this presentation, the specification of the PLANET and recent results obtained at PLANET are introduced.
Hattori, Takanori
no journal, ,
PLANET is a neutron powder diffraction beamline dedicated to high-pressure experiments, which was constructed at the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility in J-PARC. The most characteristic feature is the capability of structure analysis on crystals, liquids and amorphous solids under high-pressure and high-temperature condition ( 10 GPa, 2000K) using a large multi-anvil press ATSUHIME specially designed for pulsed neutron diffraction experiments. Additionally, the high-pressure experiments can be performed at low temperatures (
10 GPa, 2000K) using a large multi-anvil press ATSUHIME specially designed for pulsed neutron diffraction experiments. Additionally, the high-pressure experiments can be performed at low temperatures ( 77 K) using various types of presses. Because of these unique characters, the PLANET is used in various fields of sciences, such as geophysics and materials science. The details will be introduced in the presentation.
77 K) using various types of presses. Because of these unique characters, the PLANET is used in various fields of sciences, such as geophysics and materials science. The details will be introduced in the presentation.
Hattori, Takanori
no journal, ,
To discuss the specification of the high-pressure beamtime to be constructed at Cheese Spallation Neutron Source (CSNS), I introduced the details on the concept, design and performance of the high-pressure neutron diffractometer PLANET constructed at J-PARC in Japan. Besides them, tips to determine the instrumental parameters for the beamline at CSNS are introduced.
Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Machida, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Okazaki, Nobuo*; Kakizawa, Sho*
no journal, ,
PLANET is the neutron beamline dedicated to high-pressure experiments in J-PARC. One of most characteristic features is its ability to conduct diffraction measurements simultaneously at high pressures and high temperatures up to 24 GPa and 1200 K, respectively. Another characteristic feature is its ability to collect clean pattern without parasitic scattering from materials around sample by defining the diffraction gauge volume with narrow incident slits and radial collimators with a field of view of 0.8-3.0 mm at the sample position. This enables precise structure determination not only of crystals but also of liquids and amorphous solids. Furthermore, it also enables the use of smaller samples, which contributes to increase maximum available pressure. In this presentation, the performance and recent developments of the beamline will be introduced along with recent scientific results obtained at PLANET.